Introduction
The Engineering, Procurement, Construction [EPC] sector, India’s second largest economic segment is a prominent form of contracting agreement in the construction industry. Under this, the contractor will carry out the detailed engineering design of the project, procure all the equipment and materials necessary, and then construct the whole structure and deliver a functioning facility /asset to the client.
Increasing role of EPC
Over the years, the infrastructure business has witnessed several forms in which construction contracts are undertaken. Under the package based model which was adopted earlier, the time, risk, and budget used to lie with the owner/developer. However these old models of contracting have given way to new modalities with the projects becoming more complex and risk leveraging adopted by the owners. Gradually, over time, with the evolvement of EPC contracts, the onus of managing the whole project has shifted from the owner/developer to the contractor. Initially, there were only few contractors who had the required technological and financial capabilities to take overall responsibility of the complete project; therefore, large projects were divided into small EPC packages. Gradually the EPC contractors developed technical expertise and became financially competent and the project owners began to award them complete projects. The EPC contractors have carved out a niche for themselves by specializing in a particular industry. For instance, certain contractors are well known in the industry if you want to set up a bio-technology plant, oil refinery, fertilizer manufacturing units, etc.
Benefits of EPC Industry to Society:
With the increasing role of EPC sector, it is very essential to highlight some of the benefits of EPC to the society:
- Absorbs rural labour and unskilled workers (in addition to semi-skilled and skilled workers) ;
- Provides opportunity for seasonal employment thereby supplementing worker’s income;
- Permits large-scale participation of women workers ; and
- Development of Infrastructure, thereby sustaining the growth of an economy.
EPC Model
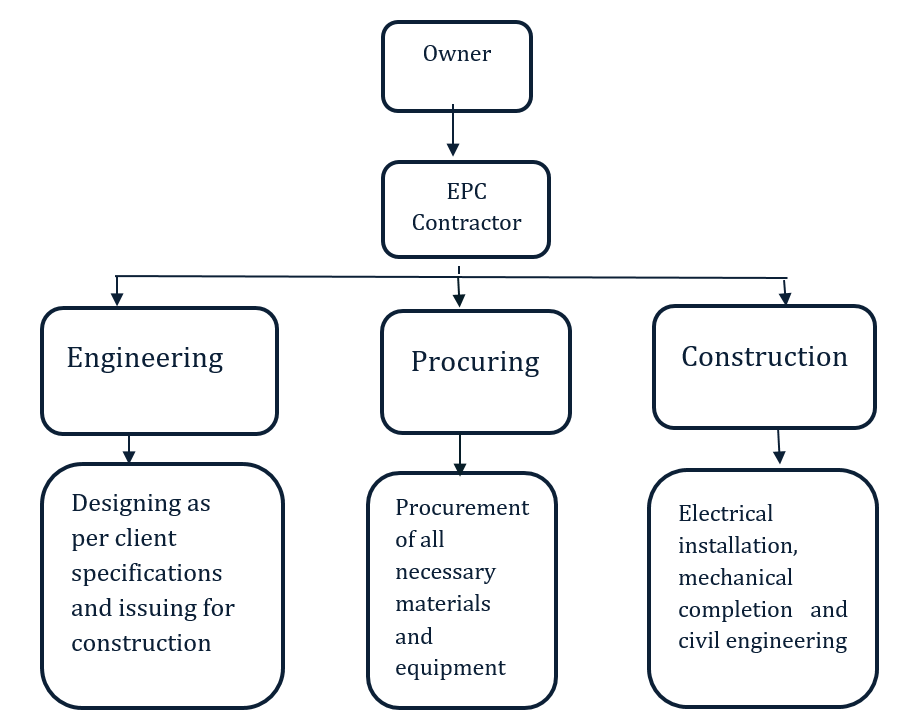
The increasing reliance by clients on EPC contracts can be highlighted as follows:
Sector | Sub-Sector | Clientele base* (government-private ratio) | Order of models adopted by Government |
Infrastructure construction | Roads | 50:50 | PPP->Annuity->EPC |
Railways | 80:20 | EPC->PPP | |
Ports | 50:50 | PPP->EPC | |
Airports | 50:50 | EPC->PPP | |
Urban infrastructure | 80:20 | EPC->limited PPP | |
Building construction | Building construction | 20:80 | Cash contracts->EPC |
Oil & Gas | Oil & gas | 80:20 | EPC |
Power | Power | 20:80 | EPC |
Specialized | Marine | 20:80 | EPC |
Hydro | 80:20 | EPC | |
Industrial | 20:80 | EPC |
The role of Internal Audit in EPC Sector
- Current Scenario:
With increased regulatory focus and widespread negative impact of frauds, the management and senior executives are increasingly concerned about the vulnerability and exposure of their organisations to frauds and whether or not they are adequately protected. This brings into focus the role of internal audit in risk management. The internal audit function is not to monitor and detect but also to investigate fraud incidences when they arise. According to the Chartered Institute of Internal Auditors, the role of internal audit is to provide independent assurance that an organisation’s risk management, governance and internal control processes are operating effectively. Unlike external auditors, they look beyond financial risks and statements to consider wider issues such as the organisation’s reputation, growth, its impact on the environment and the way it treats its employees.
Also as per Section 138 of the Companies Act 2013, internal audit is mandatory for different class of companies as specified below:

- Engineering Project Risk Management:
Internal auditors in 21st century should be experts in risk management. Effects of internal audit should not only point out existing risk in active ways but also indicate how to manage and control risk while taking precautions to curb them.

To communicate risk information timely:
The Internal Audit Report, inter alia makes the Board of Directors, those charged with governance realise how the risks are currently dealt with. In addition, internal auditors conduct risk monitoring and control evaluation to verify the effectiveness of those control.
Internal auditors can use their expertise in risk management from an independent and objective position to provide valuable assurance and consulting services, so that it enhances the level of risk management within the engineering enterprise.
Risks and their Controls in EPC Sector
- Areas with High risks
Procure to Pay [ P2P]
Procurement is one of the core functions of any project undertaken through EPC mode. It involves dealing with a variety of vendors & subcontractors along with handling huge quantities of goods & spare parts. It is also one of the most complex business process and an area prone to fraud, money leakages and inefficiencies. Since it is one of the most critical business processes which involves huge cash flows, visibility into the entire life-cycle of a transaction from vendor selection to the final invoice generation becomes a challenge for an organisation. The Association of Certified Fraud Examiners (ACFE) found that companies lose 5 percent of revenue each year to fraud, which amounts to nearly $3.7 trillion globally. Much of this fraud loss can be attributed to procurement fraud.
Frauds by different classes of people:
- By Procurement officials:
There is always a risk that the purchase managers who have personal ties to the vendors will collude & give preferential treatment to a single vendor of their choosing. They further try to ensure that the offer of the vendor is accepted by superiors within the entity.
- By Sub-contractor:
Sub-contractors use a lower grade material which may lead to subsequent change order to repair/replace later on or can even lead to a structure or system failure. There is a possibility that the materials which are used by the sub-contractor may lead to an unfavourable input/output ratio.
Activities undertaken to avoid risk:
Developing a strong resistance in entire organization through regular trainings on Ethics, Compliance & Anti-bribery would help in setting a tone against fraudulent practices.
Along with this, having a strong process on Vendor selection through Bid documents & their documentation will help in avoiding any Vendor selection biases. Rotation of procurement staff & regular site visits to verify operations by subcontractors will also keep such instances in check.
Order to Cash [ O2C]
Price escalations:
Without a price escalation clause, if there is an unexpected rise in the market price of key construction materials, a contractor will have no respite from such procurement of materials at inflated prices.
It can be further explained with the help of the following table highlighting the Wholesale Price Index:
Year/Index | 1996 | 1997 | 1998 | 1999 | 2000 | 2001 | 2002 | 2003 | 2004 | 2005 | 2006 |
Commodities | 125.6 | 131.3 | 138.9 | 143.8 | 152.8 | 160.7 | 164.7 | 173.4 | 184.9 | 193.7 | 203 |
Cement | 137 | 129.2 | 129.3 | 129.5 | 129.3 | 150.5 | 145.1 | 146.2 | 151.1 | 162.5 | 190.1 |
Steel | 121.9 | 128.4 | 132.7 | 133.9 | 136.2 | 136.6 | 140.8 | 168.3 | 222.5 | 253.5 | 246.1 |
From the above table, it is evident that between1996 to 2006, the index of cement has gone up by 39% and the index of steel has gone up by 102%. Thus, there is a need to have proper escalation clause in the EPC contracts. The basic rationale for a price escalation clause is to compensate the contractor for increase in construction costs which are beyond the control of both the parties.
Activities undertaken to avoid risk:
Properly drafted & agreed mutually between all parties to contract, Price-Escalation clause should clearly indicate the rise in the cost of a particular item vis-à-vis the rise in market price. Project or Sales team of the EPC contractor should be in charge of contract negotiations from the start.
Payroll
EPC sector is one of the largest employment generation sector for Indian economy. It provides employment to skilled, semi-skilled & unskilled labourers along with professional staff. According to the Association of Certified Fraud Examiners, Payroll fraud is number one source of accounting fraud and employee theft. Payroll Fraud happens in 27 percent of all businesses. One very glaring example of Payroll fraud was of Satyam Computers where Former Chairman of the Company had admitted siphoning off crores of rupees by paying salaries to 13,000 ghost employees.
At times, there is a possibility that there is no proper segregation and data maintenance in respect of permanent and contracted employees. Also, there can be under-booking or over-booking of time-sheet thereby resulting in incorrect booking of manpower cost. This in turn affects costs & revenues of project for a given reporting period.
Activities undertaken to avoid risk:
It is the responsibility of the HR department to have proper salary structure with grades and designations. Proper segregation and data maintenance between different categories of employees should be done since the policies, pay scale and benefits for those categories are always different in any organization. This data needs to be kept updated and maintained in master forms of all employees in hard as well as soft copy containing mainly the relevant information in a confidential manner.
Fixed Asset
For an EPC sector, in order to execute work on site, various high value equipment are required. It is also possible that many projects are progressing concurrently at different sites. Hence, it is necessary to have proper co-ordination among the site personnel and manager at HO to keep proper record of Fixed Assets in use. This generally doesn’t work well as there is huge volume of fixed assets and lack of co-ordination among the site personnel is usually observed. Thereby resulting in below mentioned risks:
- Capitalisation of asset at negative values
- Asset may be capitalized even when the asset is not ready for use / the amount at which the asset is capitalized may be incorrect / inaccurate
- Fixed asset register is not properly maintained
- Differences in FAR as per head office vis-à-vis FAR as per site
- Unauthorized transfer of asset from one location to another
Activities undertaken to avoid risk:
A proper process for fixed asset purchases, transfers / disposal should be implemented and regular reconciliations (monthly or quarterly) should be carried out. Also, Tagging of assets is very crucial, asset tag should contain unique asset codes or identification numbers, details about location, group or any other relevant association.
Treasury
Risk management is at the heart of most treasury operations and it is helpful to situate the risks managed by treasury within the overall risk map of the company. One such aspect in treasury is
Payment splitting in order to avoid higher authority approval. A higher authority approval is needed when let’s say PO amount exceeds Rs. 10,00,000/- So, for a PO of Rs 15,00,000/-; the management splits it into 2 PO of Rs 8,00,000/- and Rs. 7,00,000/- respectively to eliminate the higher authority approval.
Activities undertaken to avoid risk:
There should be a proper system to reconcile same party – same date – amount paid so as to avoid such instances.
Financial Statements Closing Procedures [FSCP]
An effective financial statement close process helps an organisation in making better and more timely decisions about the strategy and the business. Thus, FSCP is one of the important area.
EPC companies operating large engineering projects by means of their supply chains, procurement plays a key role in project execution and thus there are loads of materials coming in site premises. Especially on the cut-off date, when materials are physically received on site, GRN cannot be simultaneously updated, however entries are made in Daily Receipt Register (DRR). Therefore, a provision is booked against such materials wherein the GRN is not yet accounted.
Activities undertaken to avoid risk:
Maintain a list or register which clearly identifies that these goods are received but GRN / invoices are not booked and thus these unaccounted liabilities need to be taken into consideration while closing the financials.
Information Technology General Control (ITGC)
With the increasing IT regulations and the need for an effective and efficient IT Governance, a well-established ITGC in an organisation can leverage many complex topics. The objective of ITGC’s is to ensure the integrity of the data and processes that the systems support. Any deficiency in IT controls could severely hamper the effectiveness & efficiency of other controls placed in an organisation. Also, critical data such as pricing, profitability and strategies may get into unauthorized hands.
Activities undertaken to avoid risk:
Firstly, it is very necessary to have a fully-functional IT Department. Further,
end point protection software should be made to run on a weekly basis to detect deviations for Anti-Virus Software. Also, E-mail with instructions to identify the version of Anti-Virus system installed on each computer should be sent to users on a monthly basis.
B .Areas with Medium risks
Area | Risks Involved | Controls |
1. Procure to Pay | Unauthorized purchases are made in the name of company. | System has to be designed in such a manner that invoice should be booked against an authorized Purchase Order (PO) only. PO date should always be before the Invoice date. |
Duplicate invoices are posted in the system by mistake. | System should have a tolerance limit with regards to Invoice & PO. Eg: Invoice can be entered against a PO for 110% of PO value. | |
Unauthorized alteration of GRN. | GRN alteration rights are to be given to specific users only. Such users carry out alteration only on receipt of duly approved GRN alteration request form. Log of alterations to be maintained. | |
Registers maintained by storage yards for movement of materials are not updated. Due to which person responsible for movement of materials and person receiving and dispatching them cannot be identified. Also, Material is issued without filling the issue slip which may lead to unauthorised issue of materials. | Physical verification of materials should be conducted and registers should be updated and checked on timely basis by the store manager. Designating a specific person to fill up the issue slip at stores location & carry out material reconciliation. |
Area | Risks Involved | Controls |
2. Order to Cash | Billing break up of a project is not proper as per the contract | Scrutiny of the contract with the client to be done and ensure that design, supply and erection phase are properly billed. |
Dormant project codes exist in the system even after the project is completed. | Appropriate tagging against project codes needs to be done in order to understand the stage at which the project is. | |
Duplicate Accounts Receivable(AR)/ Customer ledgers are created | System should prompt & restrict the user whenever duplicate AR / customer ledgers are created. Unique keys like PAN, Aadhar can be used as base for identification. | |
Foreign trade receivables are restated at the incorrect foreign exchange rate. | Booking of invoice to be done on RBI daily rate which is entered by a specific person into the ERP. Difference in foreign exchange rate at the time of payment to be booked in “Exchange Gain / Loss” account. | |
3.Inventory–Scrap | Good quality material is mixed along with sale of scrap and it could also lead to a very high percentage of scrap generation. | At site, the project needs to have a dedicated area for miscellaneous work like segregation of scrap/debris ensuring that the scaffolding and other materials do not go under the debris. A proper process should be followed consisting of intimating the head of the team, project department about the scrap generated , submission of the report regarding the scrap, approvals by the respective head , disposing off the scrap, making the necessary accounting entries, updating the stock register, planning for re-procurement of such inventory. |
Area | Risks Involved | Controls |
4. Payroll | Mismatch in payment in accordance with the contract of employment | Ensure that gross pay is in accordance with contract of employment, statutory & other deductions are properly made and paid over to the concerned authorities. Proper payroll calculations to be made. |
Employees are not physically present as mentioned in the contract | Report site labour daily using electronic sign in/sign out system. Surprise site visit on pay-day to verify employees receiving payroll are not fictitious. | |
Possibility of salary being processed to employee post exit from the company | After calculation of Full and Final Settlement, “Left Date” should be updated against the exiting employee in the employee master, post which no salary payment can be booked against that employee code. | |
5. Treasury | Since there is excessive work pressure while executing a project on site, there is always some accounting backlog which may lead to no proper vouchers being generated on site and many other problems with routine work. | A proper person should be delegated to ensure that there is no backlog in the accounting process and work is completed on time and also ensuring that the company is in line with regulations is very essential. |
Area | Risks Involved | Controls |
6.Compliance | Incorrect recording of tax-liability in the books leading to non-compliance of statutory acts. | Tax-liability should be auto-calculated & booked at the time of passing the Accounts Payable entry by user department. It must be reviewed by the Project Accountant at the time of approval of AP. Deduction of taxes on provisional expenses should be undertaken by Project Accountant on an annual basis. |
7.FSCP | Provisions are booked on “inclusive of tax” basis which is incorrect. | Tax component should not be included while creating a provision as they do not form part of cost unless they are non-creditable. |
Unauthorised backdated entries recorded in the system . | Previous period should be closed in the system. Only certain users should have rights to open, close or pass back-dated entries. This must be done with the documented approval from HOD of Finance | |
Prepaid expenses are not accurately and completely recognised / Amortisation of prepaid expenses is not booked | Accounts officer must maintain excel calculation sheet of prepaid expenses. Amortization of expense is calculated as a part of book closure procedures .This sheet should be updated regularly and matched with balance as per book of accounts. | |
Compliance with Indian Accounting Standards (IND AS). | All the transactions during the IND AS transition phase are to be carried forward properly. |
Conclusion:
By establishing a well selected control framework it is possible to continuously improve the quality of multiple critical domains of an organization. It can be a crucial instrument to assure compliance to the increasing amount of mandatory and complex regulations. It is, therefore, of utmost importance that internal audit functions are adequately funded, staffed and trained with appropriate specialized skills. Routine internal audits ensure the company has the ability to survive in a competitive business environment and continue to prosper. Auditors do this by:
- Monitoring, analyzing and assessing the risks and controls of the organization
- Reviewing the organization’s compliance with the applicable policies and laws
- Making reassurances and recommendations to the organization.
Therefore, it is also imperative to have a well-defined response plan to handle potential frauds. With increasing complexity of enterprise environment, risk management techniques will develop continuously, and simultaneously, internal audit itself and corresponding audit technique will move forward, while involvement of internal audit in study on risk management will have a broader prospect in future.
Disclaimer: The views and opinions; thoughts and assumptions; analysis and conclusions expressed in this article are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect any legal standing.
Authors:
CA Aakash Mehta
Partner, MASD
E-mail ID: aakash.mehta@masd.co.in
Poojan Joshi
Associate Consultant, MASD
E-mail ID: poojan.joshi@masd.co.in
